Which of them offer special health benefits?
You can’t cook without using fats and oils, but we have to ask ourselves how healthy and digestible they really are. We use oils almost every day in every type of cooking, so let’s take a look at which of them are healthy and which could be harmful to you.
Even in ancient times, the Greeks and Romans used olive oil for frying and to refine dishes. But cooking oil didn’t reach Germany until the 20th century. Until then, the primary fat used in this country was butter.
Cold-pressed oils versus refined oils
We should use cold-pressed oils to prepare cold dishes and refined oils for cooking with heat. With a few restrictions, however, cold-pressed cooking oils can also be used for frying and deep-frying. Cold-pressed oils (also called native oils) are not refined, but instead remain in their original composition after the oilseeds have been compressed.
This explains why, for example, rapeseed oil, walnut oil and pumpkin seed oil retain theirnutty flavour. Among vegetable oils, cold-pressed rapeseed oil is a true all-rounder. It has the lowest proportion of saturated fatty acids, a high proportion of monounsaturated fatty acids and contains a lot of unsaturated omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E. Refined oils, on the other hand, are obtained through the application of heat and chemicals. Most oils come in two varieties: as cold-pressed (native) oil and as refined oil.
Olive oil, for example, is available in both variants: refined olive oil is chemically processed and retains almost none of its healthy ingredients. Cold-pressed oils are healthier than refined oils because the manufacturing process is much gentler, meaning that they retain more vitamins and flavour molecules, as well as the essential fatty acids.
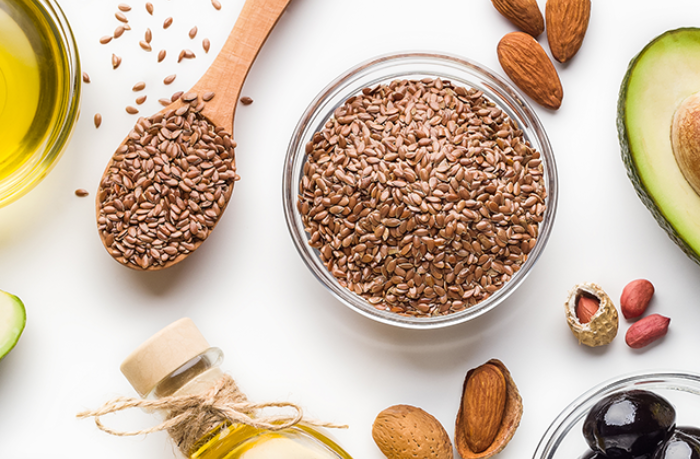
Particularly healthy oils include coconut oil, rapeseed oil, olive oil, sunflower oil, linseed oil and walnut oil. There is even such a thing as grapeseed oil, which as the name suggests is obtained from the seeds of grapes.
Rapeseed oil is particularly healthy because it is rich in unsaturated fatty acids and has a particularly favourable ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids. Linseed oil is also rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and has the best omega-3/omega-6 ratio. Cold-pressed rapeseed oil, soybean oil and safflower oil also have a very good fatty acid composition.Other suppliers of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids include walnut oil and hemp oil.
But watch out: too much of any type of oil is not necessarily healthy. Oils provide us with a lot of energy, meaning that they are high in calories.
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids
Why are they so important? Omega-3 fatty acids contain eicosanoids, which significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases through their effect on the blood vessels. The Federal Ministry of Education and Research writes:
“Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids serve as precursors for messenger substances and tissue hormones. While omega-3 fatty acids tend to contribute to the production of anti-inflammatory fat hormones, omega-6 fatty acids often serve as precursors for the body’s own synthesis of inflammatory fat hormones.
In order to keep the right balance, it is not so much a question of the total amount of oils consumed, but rather of maintaining an optimal ratio between the omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids consumed. The ratio should be around 1:5″.
Prof. Gerhard Jahreis, Emeritus at the Institute for Nutritional Sciences at the University of Jena, explains: “The decisive factor is the content of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids in the oils. A ratio of 1:2 is optimal. Of this, more than a third of the fat consumed should consist of monounsaturated fatty acids, preferably oleic acid. The polyunsaturated fatty acids should contain as many omega-3 fatty acids as possible.” Omega-3 fatty acids also have a positive effect on cholesterol levels and strengthen our immune system.
Very important: the human body cannot produce omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids itself. The only way to supply the body with them is through our nutrition, which is why they are referred to as “essential fatty acids“.
Particularly beneficial in treating rheumatism
Because of their anti-inflammatory properties, omega-3 fatty acids are particularly important for people who suffer from rheumatic diseases, who often also have cardiovascular diseases. Omega-3 fatty acids expand the blood vessels, thus reducing the risk of thrombosis. They also reduce blood lipid levels.
Vitamins in edible oils
You should know the following in advance: secondary plant substances, minerals and vitamins are only contained in cold-pressed edible oils. Compared to other foods, edible oils contain a particularly large amount of vitamin E and other minerals. Olive oil contains a range of vitamins, in particular vitamin A. It is rich in unsaturated fatty acids, and also contains abundant quantities of vitamin E. For these reasons, it is considered a particularly healthy oil. Cold-pressed sunflower oil contains many unsaturated fatty acids and is also rich in vitamin E and lecithin.
Up to 73 percent of walnut oil consists of polyunsaturated fatty acids (linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid), and it also contains a lot of lecithin, vitamin E and B vitamins, especially vitamin B6. Cold-pressed wheatgerm oil also contains a lot of vitamin E, and is rich in unsaturated fatty acids such as linoleic acid and linolenic acid.
Hazelnut oil is rich in unsaturated oleic acids and vitamins D and E. Pumpkin seed oil also has a comparatively high vitamin E content. Cold-pressed corn oil contains many essential fatty acids, especially linoleic acid and oleic acid. It also contains plenty of vitamin E.
But we shouldn’t kid ourselves: we should consume a maximum of two tablespoons of cooking oil a day, so we cannot get all the vitamins we need from it. This is why we need to keep eating plenty of fruit and vegetables.
What is each type of cooking oil best for?
Cold-pressed, unrefined rapeseed oil, for example, goes wonderfully with salad. It contains a lot of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids, and also has a delicious flavour. Rapeseed oil is also a real kitchen all-rounder; refined rapeseed oil is ideal for frying. The Stiftung Warentest even writes that rapeseed oil is healthier than olive oil. Compared to olive oil, it contains more vitamin E and a higher content of omega-3 fatty acids.
Cold-pressed extra virgin olive oil is particularly suitable for cold dishes: it can really show off its full-bodied aroma with salads or antipasti. It also goes well with all vegetables and pasta dishes. Olive oil and rapeseed oil both have high levels of oleic acid, which reduces the amount of unwanted LDL-cholesterol in the blood.
If you suffer from high cholesterol, the Heart Foundation recommends rapeseed oil, walnut oil and olive oil in particular. Oils with a high proportion of linoleic acid, such as sunflower oil or safflower oil, are less suitable.
Refined olive oil is the best choice for frying fish. If you use sunflower oil for frying, so-called aldehydes are formed in the pan, which are considered toxic in larger quantities, as scientists from the University of the Basque Country have discovered and the dpa has reported. The study was published in specialist journal Food Research International.
Pan-frying and deep-frying
Refined vegetable oils such as corn oil, rapeseed oil, sunflower oil and peanut oil are suitable for deep-frying between 175 and 190° Celsius. Only heat-stable oils with a smoking point of over 160°C should be used for frying. These are mainly refined oils such as peanut oil, olive oil, rapeseed oil and sunflower oil. Linseed oil is not suitable for pan-frying, deep-frying or baking.
Safflower and sunflower oil should only be used for cooking if you have chosen a special oil suitable for frying which has been produced from specially cultivated varieties of oil rich in oleic acid. The ideal temperatures are 130-140°C for pan-frying and 160-170°C for deep-frying. You should note: in general, refined oils are almost odourless and neutral in flavour. They have a longer shelf life than cold-pressed oils and are also cheaper.
For deep-frying French fries, sunflower oil, peanut oil and sesame oil are ideal, as they have a neutral flavour and can be heated to 210 degrees. Coconut oil can also be used for deep-frying, but coconut oil, palm oil and palm kernel oil contain large amounts of saturated fatty acids, which have a particularly negative effect on our blood lipids.
Argan oil, the most expensive oil in the world
The most expensive oil in the world is argan oil. It is obtained from the seeds of the argan tree’s ripe fruit. The oil is expensive because the entire production, from picking to pressing the fruit, is done by hand. Argan oil is only found in Morocco, and is considered the country’s liquid gold.
Argan oil is used in gastronomy as well as in cosmetics and hair care. The oil has a very high proportion of natural antioxidants that protect against free radicals.
You should also note: all oils should be stored in a cool, dark place, and you should never pour fats or oils down the drain or flush them down the toilet. Fat is not soluble in water, so it remains in the drainage pipes and can cause blockages.
So, let’s head to the kitchen and make a nice, tasty salad.
Stay healthy!